Risk Management System
This system is formulated in reference to the "Guidelines for Risk Management Practices of Futures Dealers" and the "Self-Inspection Table for Establishing Risk Management Mechanisms by Futures Dealers" promulgated by the Taiwan Futures Exchange.
To effectively manage the company's operational risks, establish a management process that is observed and adhered to by all levels, and jointly promoted and implemented by the board of directors, managers at all levels and employees. From the company's overall perspective, through a series of activities such as identification, measurement, monitoring, response and reporting, quantify risk management with qualitative and rigorous measurement models to rationalize the allocation of risk assets and maximize shareholder returns within the company's risk tolerance.
- Formulate risk management policies and establish qualitative and quantitative management standards, promptly report the implementation of risk management to the board of directors, and make necessary improvement suggestions.
- Evaluation and decision-making on business operation strategies
- Approve business applications and authorize transactions
- Ensure the effectiveness of risk management and bear the ultimate responsibility for risk management.
- Report to the board of directors on the risk assessment and trading performance of the board's holdings and the achievement of target goals.
- In case of any abnormal market value assessment (such as when the holding position exceeds the total loss limit), it should be reported to the board of directors immediately, and the business unit should be requested to take necessary countermeasures.
- Assist in formulating risk management systems.
- Assist in formulating risk limits and allocation methods for each department.
- Ensure the implementation of risk management systems approved by the board of directors.
- Submit timely and complete risk management reports to the chairman, vice chairman, and general manager.
- Before engaging in various transactions in business units, they should first understand the content of the relevant transactions and continuously monitor the holding positions of the completed transactions.
- For financial instruments with quantifiable risks, risk management measurement techniques should be improved as much as possible.
- Have a thorough understanding of the risk limits and usage of each business unit.
- Assess the company's risk exposure and risk concentration.
- Development and execution of stress testing and backtesting methods
- Evaluate the discrepancy between the actual profit and loss and the forecast of the investment portfolio.
- Review the commodity pricing models and valuation systems used by business units.
- Other risk management related matters
- Ensure the timely and accurate communication of risk management information.
- Ensure that business units (subsidiaries) effectively implement the relevant provisions of various risk limits.
- Monitor risk exposure and report exceedances, including actions taken by business units (subsidiaries) to address exceedances.
- Ensure that internal control procedures within business units (subsidiaries) are effectively implemented to comply with regulatory requirements and risk management systems.
- Overall responsibility for all risk management matters related to its subordinate units (subsidiaries). Responsible for monitoring operational risks within business units (subsidiaries) and implementing various countermeasures.
- Oversee the communication of risk management information.
- Regularly assess the effectiveness of internal controls over commodity transactions in business units.
- Review the implementation of the company's risk management system and disclose the actual situation in the audit report. For deficiencies or abnormalities found during the inspection, they should be tracked after the review of the audit report, and regular tracking reports should be prepared to ensure that relevant units have taken timely and appropriate corrective measures.
- Responsible for auditing the compliance of various regulations and laws.
- Process accounting transactions and manage funds in accordance with approved contracts and trading documents.
- Establish provisions for off-balance-sheet transactions.
- Obtain price information from a pricing system independent of the trading department to revalue positions held.
- Completed transactions should be recorded in the accounts and recognized in profit or loss on a timely basis.
- Make announcements in accordance with the regulations of the competent authority.
- Customer credit check before trading account opening.
- Custody and storage of account opening and trading agreements.
- Delivery and settlement of commodities.
- Execution of margin call and recovery for insufficient customer margin.
- Reporting of trading contracts to relevant regulatory authorities.
- Confirmation of trade details.
- Post-trade credit monitoring for special customers.
- Consulting with legal counsel to discuss relevant management policies.
- Trading contracts/agreements must undergo legal compliance and legal department review of all rights and obligations, legality, and related legal documents before being signed with counterparties.
- The external contract seal application form must be reviewed and approved by the Legal Compliance and Legal Department.
- Overseeing legal and regulatory compliance.
- Supervising business units to assess the impact of newly promulgated regulations on the company's business.
- Before launching new products, services, or applying for new business lines, the Legal Compliance and Legal Department Head shall issue an opinion in accordance with laws and regulations and internal standards and sign for responsibility.
The company's risk management process includes:Risk identification、Risk assessment、Risk monitoring、Risk reporting、Risk response measures.
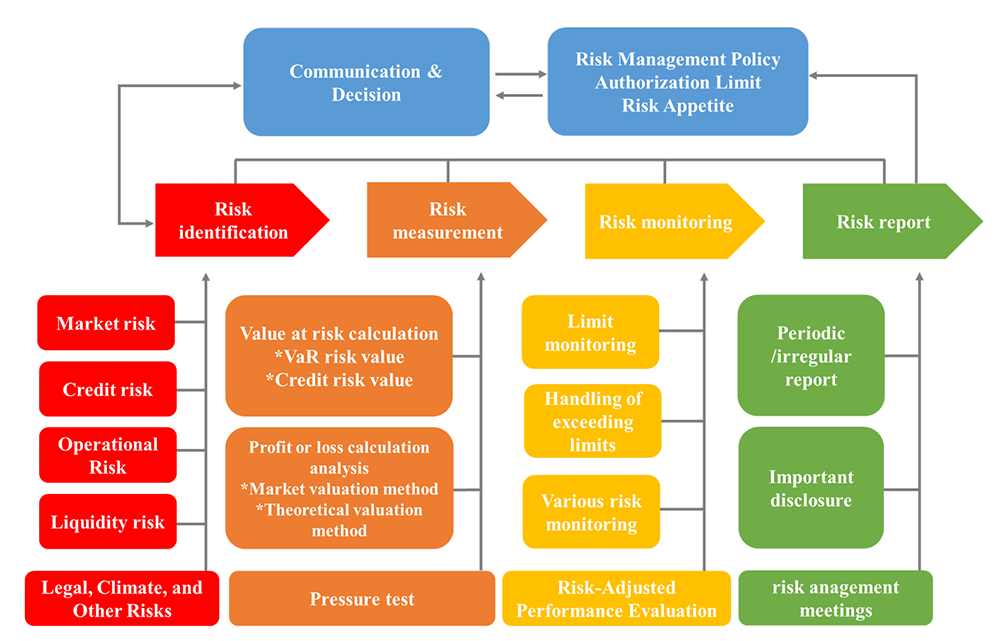
Based on the characteristics of the industry, the main risks that the company's operations may face are market risk, credit risk, liquidity risk, operational risk, and legal and other risks. Climate change will directly or indirectly impact the company's finances, strategies, operations, and products. The company should identify the correlation between climate risk and credit risk, market risk, liquidity risk, and operational risk, and review the emerging regulatory measures arising from climate risk and their impact on the company's reputation and legal obligations.
Market risk refers to the risk of loss arising from fluctuations in market prices of financial assets, such as interest rates, exchange rates, equity securities, and commodity prices, over a given period. These fluctuations can lead to losses in both on-balance sheet and off-balance sheet items.
Credit risk refers to the risk of loss arising from the possibility that a counterparty (including issuers, contractual counterparties, or debtors) fails to fulfill its obligations, and this default causes losses to the issuer's risk exposure or financial condition.
Liquidity risk refers to the risk of loss arising from the inability to readily convert assets into cash or obtain sufficient funds to meet maturing obligations (known as "funding liquidity risk") and the risk of significant market price fluctuations when dealing with or offsetting positions due to insufficient market depth or disruption (known as "market liquidity risk").
Operational risk refers to the risk of loss arising from direct or indirect losses caused by internal processes, personnel, and systems failures or errors, or by external events.
Legal risk refers to the risk of loss arising from non-compliance with government regulations, invalidity of contracts due to lack of legal enforceability, unauthorized actions, omissions in contractual terms, or inadequate regulations, which could lead to potential losses.
Climate risk refers to the transition risks and physical risks that may arise from climate change and the transition to a low-carbon economy. Transition risks can impact a company's finances, strategies, operations, products, and reputation, while physical risks can affect a company's finances and operations due to extreme weather events.
Other risks include strategic risk (business risk) and reputational risk.
-
Quantitative Measurement of Market Risk
Statistical Basis Measurement Method: The Value at Risk (VaR) for linear products (stocks) is calculated using the Variance-Covariance method (RiskMetrics Approach--EWMA) to determine the maximum potential risk for the next business day’s portfolio at a specified confidence level. For non-linear products (options), the Value at Risk is calculated using the Delta-Gamma Approximations method, offsetting the risks of each trading contract to determine the maximum potential risk for the next business day’s portfolio at a specified confidence level. To verify the accuracy of the model estimation, backtesting is conducted by testing the previous day's actual P&L (T-1 day P&L) against the originally estimated VaR to check the number of breaches within a year.
Sensitivity analysis measures the sensitivity of held positions to individual risk factors (e.g., interest rates and exchange rates). Our company's sensitivity analysis of exchange rate fluctuations includes evaluation and analysis of our own overseas funds and the fee income from foreign futures products.
Stress testing is used to simulate and measure the impact of abnormal market changes on the value of a portfolio, serving as the basis for formulating response measures. Currently, the stress testing targets for the portfolio are based on a ±10% change in the weighted index or the stock prices of the underlying securities.
The risk control of our company's proprietary positions includes:- Loss limit control - Based on each trader's trading strategy and capital allocation, monthly, quarterly, and annual loss limits are set. Additionally, the department's monthly, quarterly, and annual loss limits are also established.
- Margin limit control - The upper limit of capital usage for intraday and overnight positions.
- Position limit and Open Delta value control - Calculating the position limit and Open Delta value limit for each trader's positions and the overall positions.
- Margin ratio control for domestic and foreign futures trading open positions (the initial margin required for open positions in futures contracts, options contracts, and futures options contracts based on domestic securities, securities portfolios, or stock price indices, plus the premiums paid for options contracts, minus the premiums received for options contracts) - The domestic futures market portion must not be less than 200% of the foreign futures market portion.
- Option trade price verification - Using the option abnormal trade query to compare the implied volatility of each executed and offset position with the settlement price implied volatility to check for abnormalities.
-
Quantitative measurement of credit risk
Credit risk is the potential financial loss that a lender may incur due to the borrower's inability or unwillingness to repay their debt obligations. To effectively manage credit risk, financial institutions employ various methodologies to assess and quantify the potential losses associated with their lending activities.
Our company's credit risk management includes:- Pre-Transaction Credit Assessment and Creditworthiness Verification: Before entering into any transaction, parties should carefully assess the creditworthiness of their counterparties and verify the legality of the transaction.
- Credit Tiered Management: Special monitoring is applied to transactions with customers of special credit standing.
- Post-Transaction Credit Monitoring: Regularly review the creditworthiness of different customers and their positions, including their profit and loss status, and periodically evaluate and supervise various credit enhancement measures (including collateral).
- Other effective measures to reduce credit risk include collateral, guarantees, and credit risk netting agreements.
-
Liquidity Risk Measurement
Market Liquidity Risk Management:
To avoid losses caused by market liquidity risk, our company quantitatively manages market liquidity risk for the concentration of business units and investment positions in our own funds, as well as the general market trading volume. In addition, there is an upper limit on the holding amount of securities issued by a single company, so as to effectively control market liquidity risk.
Liquidity risk management:
The Treasury is an independent funding unit from each business unit. In order to control liquidity risk and consider the funding needs of various products and different domestic and foreign markets, the Treasury prepares "Upfront Margin Deposit and Withdrawal Table", "Securities Trading Application Form", "Customer Futures Margin and Rights and Interests Special Account In and Out Form" and other management reports daily after review and approval by a special person and archived for inspection. -
Quantitative Measurement of Operational Risk
Operational risk encompasses the risk of direct or indirect losses arising from internal personnel, operational processes and information systems, and external events. It is equally important as market risk, credit risk, and liquidity risk, and requires the collection and organization of relevant operational risk data (including: occurrence time, event type, document records, and loss status) for appropriate quantitative measurement and management.
Our company has established an internal control system, and the internal audit department regularly conducts regular audits and special audits in accordance with the standardized procedures and control points to manage operational risks in business and transaction processes. - With respect to the risks posed by climate change, the company's management should be responsible for developing and implementing response strategies and plans, reporting regularly to the board of directors, and providing the board with relevant climate risk management information.
- For other risks that are currently difficult to quantify, such as legal risks, strategic risks, and reputational risks, appropriate risk management measures and qualitative risk measurement should also be taken to achieve the goal of risk management.
To monitor the usage of various risk limits and their exceedances in order to facilitate the implementation of response measures, and to understand and evaluate the implementation of these measures, the Risk Management Office, business unit heads, and responsible persons and middle managers (risk control personnel) of other subsidiaries will jointly monitor risks.
The Risk Management Office monitors the risk limits for the entire company, each business unit, and each product on a daily basis, including market risk, credit risk, and funding liquidity risk, in accordance with the annual operating plan and risk management regulations. If any risk limits are exceeded, the business unit (subsidiary) is required to take immediate corrective action and report to the Internal Audit Department. The Risk Management Office is responsible for counting the number of times that trading units exceed their limits each month. For other units, the Internal Audit Department counts the number of times that they exceed their limits each month and includes this in the department's monthly KPI performance evaluation.
Business unit managers (subsidiary heads) should ensure the accuracy and effectiveness of the transaction reports they prepare. All transactions must be properly recorded in accordance with company and regulatory standards and reported as required. Our company's risk management reporting mechanism includes:
- The Risk Management Office prepares a "Risk Management Daily Report" every day, which reviews the exposure of all products across the company to market risk, credit risk, and liquidity risk, and compares it to the current regulatory limits. The report is submitted to the Chairman, President, and relevant departments via email.
- The General Manager holds regular weekly meetings with the trading departments to review their positions and profit and loss performance on a case-by-case basis.
- Heads of each department regularly participate in bi-weekly meetings and monthly business meetings, where each department reports on their work progress and reviews any abnormal situations.
After evaluating and aggregating risks, our company employs the following response measures to address the identified risks:
- Risk Avoidance: The implementation of measures to avoid any activities that could potentially introduce risk.
- Risk Reduction: The implementation of measures to mitigate the impact and/or likelihood of risks that have already occurred or may occur in the future.
- Risk Sharing: The process of transferring a portion or all of a risk to another party through various means.
- Risk Acceptance: The decision to retain a risk without taking any action to modify its likelihood or impact.
When responding to risks, careful consideration must be given to those with a low probability of occurrence but a potentially significant impact on the company's survival. The goal of our company's risk management is to maximize shareholder value within the range of acceptable risk.
Commonly used RAPM (Risk-Adjusted Performance Measurement) metrics internationally include Risk-Adjusted Return on Capital (RAROC), Shareholder Value Added (SVA), and the Sharpe Ratio.
RAPM = Profit / Economic Capital
Economic capital refers to the minimum amount of cash reserves that a company must maintain to ensure its sustainable operations.
Due to the complexity of measuring economic capital/risk capital, which requires considering and quantifying all potential risks, the company's current performance evaluation for business units is based on the concept of "risk-adjusted return." Performance compensation is calculated by deducting the cost of capital provided by the company, the allocation of costs from internal support departments, and provisions for potential risk losses. For example, a certain percentage of loss reserves is required for profits from proprietary securities trading, and a certain percentage of credit loss reserves is required for brokerage commission income. This approach aims to reflect the true operating performance of each business unit and maximize profits within the predetermined risk tolerance level.
The goal of risk-based performance management is to evaluate the performance of each unit on a consistent basis, taking into account the risks of different businesses in the evaluation process, and using this as the basis for capital allocation.
In accordance with regulatory requirements, our company reports our Adjusted Net Capital (ANC) ratio on a daily basis.
ANC = Adjusted Net Capital Amount / Total Customer Margin Required for Unoffset Positions of Futures Trader
Our company has entered into an information services agreement with our corporate headquarters and has joined the corporate-led information security management committee. Our Risk Management Information System (RMIS) was developed with the assistance of the corporate IT department and incorporates three critical aspects: application, data, and technical.
Our Risk Management Information System (RMIS) currently covers securities, futures, and options. Upon completion, the overall system will encompass: market risk, credit risk, liquidity risk, and partial operational risk management, capital allocation, asset-liability management, and performance evaluation.
Our company's risk management information system is currently developed based on our own needs. The financial systems department of our parent company's IT department has established a risk control team to be responsible for the development and maintenance of the risk management information system. The development of the risk control system software is initiated by the demand unit, and users participate to confirm the content and functions of each demand. After the development is completed, users will first test in the test environment to confirm that there is no problem before moving to the formal environment for execution. The IT department of the head office regularly meets with the business units of our company to discuss the functions that should be added or improved to the various information systems.
The valuation models used in the risk management information system are the same as those used by the business units. The risk management department is responsible for writing the calculation programs using financial engineering software, and the IT department then integrates them into the risk management information system. The main valuation models for equity-related options are Black-Scholes, Binomial, and Monte Carlo Evaluation.
- User-entered data is subject to review by risk control personnel and back-office supervisors according to the data security level, or by the heads of other relevant departments before taking effect.
- Data imported from the trading system has already undergone verification and confirmation procedures within the trading system and takes effect immediately upon import.
- Data automatically transferred by the risk management information system is automatically compared by the system based on data characteristics and data sources. If an anomaly occurs, the system administrator is notified for handling.
Define different user groups and roles based on user business characteristics and permission scope (the functions that can be performed also define the amount of data that can be queried), and the system provides the programs that can be executed and the data query scope based on the groups and roles.
The Risk Management Information System (RMIS) is designed to be accessed only by authorized Intranet users. To protect against unauthorized access and cyberattacks, the RMIS utilizes a firewall to block external connections.Data backup is currently performed using CA BrightStor backup software to safeguard all programs and data. The backup process is initiated automatically by a scheduled program. CA TNG is employed to monitor the backup execution and prevent backup failures. In the event of any anomalies, the system notifies IT personnel via email and SMS for prompt resolution.
The recovery procedure can be divided into application file corruption recovery and database corruption recovery operations. If an executable file corruption occurs, the standard procedure is to first stop the website service process, then restore the backup file to the web server, and then restart the website service process. Currently, the risk management information system uses Microsoft SQL Server as the data storage device. If a data file corruption causes the system to malfunction, the standard procedure is to first stop the database service process, then back up the corrupted file, then restore the previous day's backup data to the database server, and then restart the database service process. The risk management information system has built a backup system in the Taoyuan data center.
In addition to the relevant information required to be disclosed by the relevant supervisory authority, our company will disclose qualitative and quantitative information related to risk management in our sustainability report, annual report, financial reports, or on our company website or other appropriate locations.




